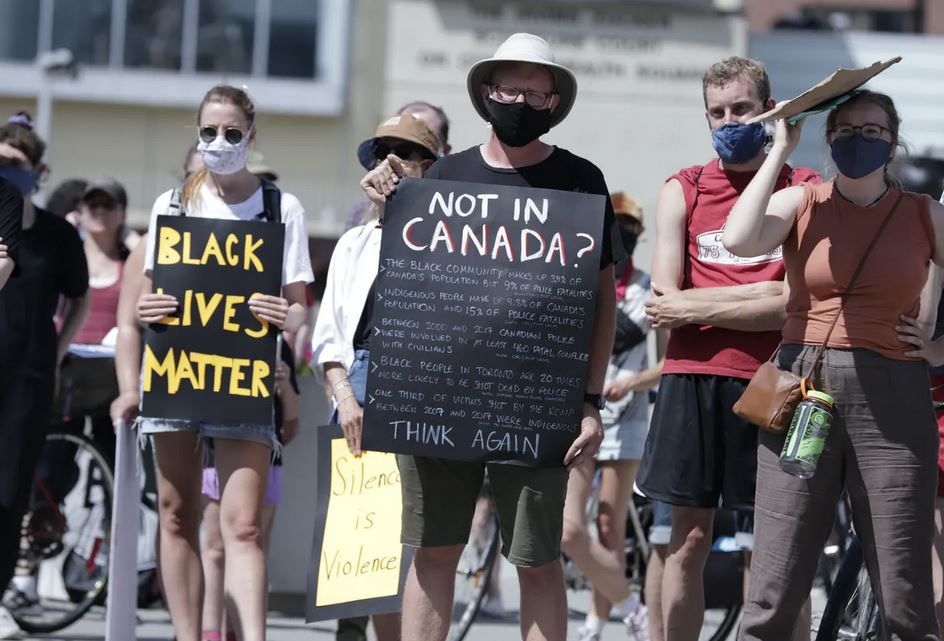Racism & the Americanization of Canadian history: Why we shouldn’t look at ourselves through a U.S. lens
On April 20, a jury in Minnesota found Derek Chauvin guilty of second-degree unintentional murder, third-degree murder and second-degree manslaughter in the killing of George Floyd. Following the verdict, Canadian media was filled with extensive coverage and endless analyses of the story.
Many Canadians watched the racism unfold in the United States with a sense of moral superiority and relief that “this kind of thing does not happen in Canada.” The Canadian response to racism south of the border can be described as an Americanization of Canadian history. The media’s lack of coverage of racism in Canada, in its historically accurate context, is a cause for concern.
Different histories of racism
Canada’s history of racism is different than the United States.
In 1619, the first slave ship docked on North American shores, bringing 20 enslaved Africans. This was the start of the transatlantic slave trade that saw at least 300,000 Africans brought to and sold at U.S. ports. Historians estimate that in Canada, between 1671 and 1834, there were 4,200 slaves – about two-thirds were Indigenous and one-third were Black.
Outlawing the slave trade and restrictions on non-European immigration later slowed down the growth of the Black population both in the U.S. and in Canada.
Immigration regulations introduced in 1962 in Canada eliminated preferences for immigrants of European origin for a points-based system, prioritizing skilled labour. As a result, the immigrant population became more diverse in Canada. Similarly, in the U.S., the Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965, the Refugee Act of 1980 and the Immigration Act of 1990 have helped to increase the number of immigrants in the country.
Immigrants today account for 13.7 per cent of the U.S. population compared to 22 per cent in Canada.
The history of slavery and immigration provides an important context to contemporary conversations on racism. But an increase in immigration does not automatically lead to more or less racism.
In a country like Canada, it’s important for us to acknowledge our differences in history from the U.S., account for racism within a particular historical context and reflect on what racism actually looks like here.
Difference can provide a space for understanding the implication of race in defining the various experiences of racialized groups, instead of a universalized representation of race and racism.
Racism towards Indigenous people
Canada has a long history of racism towards Indigenous people - from the colonization of their land and enslavementto the violation of treaties and policies that led to residential schools and the ‘60s Scoop.
Abuse and racism suffered by First Nations, Inuit and Métis people at the hands of the government continue to take a toll on Indigenous lives. Many remote communities face challenges accessing basic necessities like clean drinking water.
Indigenous people in Canada also experience the highest levels of poverty: 25 per cent of Indigenous people live in poverty while 40 per cent of Indigenous children live in poverty.
Accessing health care has also been a challenge for many First Nations people. Several months ago, Joyce Echaquan died in a hospital in Joliette, Que. Not only did she not receive the help she needed, but hospital staff told her that she would be better off dead. Meaningful action to fight the systemic racism Indigenous people are experiencing is yet to come.
In the U.S., genocidal policies aimed at Indigenous people changed when legislators passed a number of laws, most importantly the Indian Self-Determination and Education Assistance Act of 1975, which resulted in the U.S. government’s recognition of Indigenous statehood.
In recent years, some policies, especially those implemented by former president Donald Trump’s administration, have been diminishing tribal land rights, sovereignty and resources. The Keystone XL Pipeline project, approved by the Trump administration and cancelled by U.S. President Joe Biden, was met with strong resistance from Indigenous people in Canada and the U.S. The project had the backing of Canadian government.
Comments
There are 0 comments on this post